SMoon 11 15 16 3AM-1-2
Distance[edit]
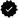
The Moon's distance varies each month between approximately 357,000 and 406,000 kilometers (222,000 and 252,000 mi) because of its ell...
Read more
Distance[edit]
The Moon's distance varies each month between approximately 357,000 and 406,000 kilometers (222,000 and 252,000 mi) because of its elliptical orbit around the Earth (distances given are centre-to-centre).[10][11][12]
A full moon at perigee is visually larger up to 14% in diameter and shines 30% brighter than one at its farthest point, or apogee.[13]
Terminology[edit]
The name supermoon was coined by astrologer Richard Nolle in 1979, arbitrarily defined as:
... a new or full moon which occurs with the Moon at or near (within 90% of) its closest approach to Earth in a given orbit (perigee). In short, Earth, Moon and Sun are all in a line, with Moon in its nearest approach to Earth.[14]
Nolle also claimed that the moon causes "geophysical stress" during the time of a supermoon. Nolle never outlined why he chose 90%.[4]
The term supermoon is not used within the astronomical community, which uses the term perigee-syzygy or perigee full-new moon.[15] Perigee is the point at which the Moon is closest in its orbit to the Earth, and syzygy is when the Earth, the Moon and the Sun are aligned, which happens at every full or new moon. Hence, a supermoon can be regarded as a combination of the two, although they do not perfectly coincide each time.
Frequency[edit]
The full moon cycle is the period between alignments of the lunar perigee with the sun and the earth, which is about 13.9443 synodic months (about 411.8 days). Thus approximately every 14th full moon will be a supermoon. However, halfway through the cycle the full moon will be close to apogee, and the new moons immediately before and after can be supermoons. Thus there may be as many as three supermoons per full moon cycle.
Since 13.9443 differs from 14 by very close to 1⁄18, the supermoons themselves will vary with a period of about 18 full moon cycles (about 251 synodic months or 20.3 years). Thus for about a decade the largest supermoons will be full, and for the next decade the largest supermoons will be new.
Effect on tides[edit]
The combined effect of the Sun and Moon on the Earth's oceans, the tide,[16] is greatest when the Moon is either new or full.[17] At lunar perigee the tidal force is somewhat stronger,[18] resulting in perigean spring tides. But even at its most powerful this force is still relatively weak[11] causing tidal differences of inches at most.[19]
As the tidal force follows an inverse-cube law, that force is 19% greater than average.[citation needed] However, because the actual amplitude of tides varies around the world, this may not translate into a direct effect.
Natural disasters[edit]
There has been media speculation that natural disasters, such as the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami and the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami, are causally linked with the 1–2 week period surrounding a supermoon.[20][21] A large, 7.5 magnitude earthquake centred 15 km north-east of Culverden, New Zealand at 00:03 NZDT on November 14, 2016, also coincided with a supermoon.[22][23] No evidence has been found of any correlation between supermoons with major earthquakes.[24][25][26]
Read less
The Moon's distance varies each month between approximately 357,000 and 406,000 kilometers (222,000 and 252,000 mi) because of its elliptical orbit around the Earth (distances given are centre-to-centre).[10][11][12]
A full moon at perigee is visually larger up to 14% in diameter and shines 30% brighter than one at its farthest point, or apogee.[13]
Terminology[edit]
The name supermoon was coined by astrologer Richard Nolle in 1979, arbitrarily defined as:
... a new or full moon which occurs with the Moon at or near (within 90% of) its closest approach to Earth in a given orbit (perigee). In short, Earth, Moon and Sun are all in a line, with Moon in its nearest approach to Earth.[14]
Nolle also claimed that the moon causes "geophysical stress" during the time of a supermoon. Nolle never outlined why he chose 90%.[4]
The term supermoon is not used within the astronomical community, which uses the term perigee-syzygy or perigee full-new moon.[15] Perigee is the point at which the Moon is closest in its orbit to the Earth, and syzygy is when the Earth, the Moon and the Sun are aligned, which happens at every full or new moon. Hence, a supermoon can be regarded as a combination of the two, although they do not perfectly coincide each time.
Frequency[edit]
The full moon cycle is the period between alignments of the lunar perigee with the sun and the earth, which is about 13.9443 synodic months (about 411.8 days). Thus approximately every 14th full moon will be a supermoon. However, halfway through the cycle the full moon will be close to apogee, and the new moons immediately before and after can be supermoons. Thus there may be as many as three supermoons per full moon cycle.
Since 13.9443 differs from 14 by very close to 1⁄18, the supermoons themselves will vary with a period of about 18 full moon cycles (about 251 synodic months or 20.3 years). Thus for about a decade the largest supermoons will be full, and for the next decade the largest supermoons will be new.
Effect on tides[edit]
The combined effect of the Sun and Moon on the Earth's oceans, the tide,[16] is greatest when the Moon is either new or full.[17] At lunar perigee the tidal force is somewhat stronger,[18] resulting in perigean spring tides. But even at its most powerful this force is still relatively weak[11] causing tidal differences of inches at most.[19]
As the tidal force follows an inverse-cube law, that force is 19% greater than average.[citation needed] However, because the actual amplitude of tides varies around the world, this may not translate into a direct effect.
Natural disasters[edit]
There has been media speculation that natural disasters, such as the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami and the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami, are causally linked with the 1–2 week period surrounding a supermoon.[20][21] A large, 7.5 magnitude earthquake centred 15 km north-east of Culverden, New Zealand at 00:03 NZDT on November 14, 2016, also coincided with a supermoon.[22][23] No evidence has been found of any correlation between supermoons with major earthquakes.[24][25][26]
Read less
Views
46
Likes
Categories
Same photographer See all
Discover more photos See all