
boonhongchan
FollowWhite Spotted Jellyfish (Phyllorhiza punctata)
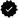
White-Spotted Jellyfish (Phyllorhiza punctata)
Phyllorhiza punctata is a species of jellyfish, also known as the floating bell, Australian spotted ...
Read more
White-Spotted Jellyfish (Phyllorhiza punctata)
Phyllorhiza punctata is a species of jellyfish, also known as the floating bell, Australian spotted jellyfish or the white-spotted jellyfish. It is native to the West Pacific from Australia to Japan, but has been introduced widely elsewhere. It feeds primarily on zooplankton. P. punctata average 45–50 centimetres (18–20 in) in bell diameter but in October 2007, one 72 cm (28 in) wide, perhaps the largest ever recorded, was found on Sunset Beach, North Carolina.
Decription
True jellyfish go through a two-stage life cycle which consists of a medusa stage (adult) and a polyp stage (juvenile). In the medusa stage male jellyfish release sperm into the water column and the female jellyfish gathers the sperm into her mouth where she holds the eggs. Once fertilization occurs and larvae are formed they leave their mother and settle to the ocean floor. Once on the bottom a polyp form occurs and this form reproduces asexually by “cloning” or dividing itself into other polyps. Jellyfish can live for up to five years in the polyp stage and up to two years in the medusa stage(active).
When found in warm waters these jellyfish flourish. They are mostly euryhaline but low salinities may have a negative effect on the species. In times of low salinity these jellyfish exhibit loss of their zooxanthellae.
They have only a mild venom and are not considered a threat to humans. They have a mild or non-noticeable sting which can be cured with vinegar. Salt water can be used as a last resort.
Invasive species
The species has been found in the waters off the Hawaiian Islands since at least 1945, in the Mediterranean Sea since at least 1965, and in large numbers in the Gulf of Mexico since 2000. While it is not known how it was introduced to these regions, it has been theorized that budding polyps may have attached themselves to ships, or were carried in a ship's ballast tank which was subsequently dumped. As an invasive species, it has become a threat to several species of shrimp. In Gulf waters, the medusae grow to unusually large size, upwards of 60 cm (24 in) across.
In July 2007 smallish individuals were seen in Bogue Sound much further north along the North Carolina coast. However, their ability to consume plankton and the eggs and larvae of important fish species is cause for concern. Each jellyfish can filter as much as 50,000 litres (13,000 US gal) of seawater per day. While doing that, it ingests the plankton that native species need.
It has also been spotted off the Southern California coast, but its presence there has not yet been confirmed.
[Credit: en.wikipedia.org-]
Read less
Phyllorhiza punctata is a species of jellyfish, also known as the floating bell, Australian spotted jellyfish or the white-spotted jellyfish. It is native to the West Pacific from Australia to Japan, but has been introduced widely elsewhere. It feeds primarily on zooplankton. P. punctata average 45–50 centimetres (18–20 in) in bell diameter but in October 2007, one 72 cm (28 in) wide, perhaps the largest ever recorded, was found on Sunset Beach, North Carolina.
Decription
True jellyfish go through a two-stage life cycle which consists of a medusa stage (adult) and a polyp stage (juvenile). In the medusa stage male jellyfish release sperm into the water column and the female jellyfish gathers the sperm into her mouth where she holds the eggs. Once fertilization occurs and larvae are formed they leave their mother and settle to the ocean floor. Once on the bottom a polyp form occurs and this form reproduces asexually by “cloning” or dividing itself into other polyps. Jellyfish can live for up to five years in the polyp stage and up to two years in the medusa stage(active).
When found in warm waters these jellyfish flourish. They are mostly euryhaline but low salinities may have a negative effect on the species. In times of low salinity these jellyfish exhibit loss of their zooxanthellae.
They have only a mild venom and are not considered a threat to humans. They have a mild or non-noticeable sting which can be cured with vinegar. Salt water can be used as a last resort.
Invasive species
The species has been found in the waters off the Hawaiian Islands since at least 1945, in the Mediterranean Sea since at least 1965, and in large numbers in the Gulf of Mexico since 2000. While it is not known how it was introduced to these regions, it has been theorized that budding polyps may have attached themselves to ships, or were carried in a ship's ballast tank which was subsequently dumped. As an invasive species, it has become a threat to several species of shrimp. In Gulf waters, the medusae grow to unusually large size, upwards of 60 cm (24 in) across.
In July 2007 smallish individuals were seen in Bogue Sound much further north along the North Carolina coast. However, their ability to consume plankton and the eggs and larvae of important fish species is cause for concern. Each jellyfish can filter as much as 50,000 litres (13,000 US gal) of seawater per day. While doing that, it ingests the plankton that native species need.
It has also been spotted off the Southern California coast, but its presence there has not yet been confirmed.
[Credit: en.wikipedia.org-]
Read less
Views
81
Likes
Awards
Brilliant
Categories
Same photographer See all
Discover more photos See all










































