
JMcCombie
FollowWinter Lilac
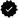
Blue colorwashed-colourwashed digital painting by J. McCombie.
Hoar frost covers lilac bush in the hay field.
Frost is the solid deposition of water...
Read more
Blue colorwashed-colourwashed digital painting by J. McCombie.
Hoar frost covers lilac bush in the hay field.
Frost is the solid deposition of water vapor from humid air. It is formed when the temperature of a solid surface is below the freezing point of water and also below the frost point. The size of frost crystals varies depending on the time they have been building up and the amount of water vapour available. Frost crystals are translucent, but scatter light in many directions, so that a coating of frost appears white. There are many types of frost, such as radiation and window frost. Frost may damage crops or reduce future crop yields, hence farmers may take measures to prevent it forming.
Hoar frost (also called radiation frost or hoarfrost or pruina) refers to the white ice crystals, loosely deposited on the ground or exposed objects, that form on cold clear nights when heat is lost into the open sky causing objects to become colder than the surrounding air. A related effect is flood frost or frost pocket which occurs when air cooled by ground-level radiation losses travels downhill to form pockets of very cold air in depressions, valleys, and hollows. Hoar frost can form in these areas even when the air temperature a few feet above ground is well above freezing. Nonetheless the frost itself will be at or below the freezing temperature of water.
Hoar frost may have different names depending on where it forms. For example, air hoar is a deposit of hoar frost on objects above the surface, such as tree branches, plant stems, wires; surface hoar is formed by fernlike ice crystals directly deposited on snow, ice or already frozen surfaces; crevasse hoar consists of crystals that form in glacial crevasses where water vapour can accumulate under calm weather conditions; depth hoar refers to cup shaped, faceted crystals formed within dry snow, beneath the surface.
The name hoar comes from an Old English adjective for showing signs of old age, and is used in this context in reference to the frost which makes trees and bushes look like white hair. It may also have association with hawthorn when covered in its characteristic white spring blossom.
Surface hoar is a cause of avalanches when it forms on top of snow. Conditions are ideal for the formation of hoarfrost on cold clear nights, with a very light wind that is able to circulate more humidified air around the snow surface. Wind that is too abrupt will destroy the crystals. When buried by subsequent snows they may remain standing for easy identification, or become laid down, but still dangerous because of the weakness of the crystals. In low temperatures surface hoar can also be broken apart and blown across the surface forming yukimarimo.
Hoar frost also occurs around man-made environments such as freezers or industrial cold storage facilities. It occurs in adjacent rooms that are not well insulated against the cold or around entry locations where humidity and moisture will enter and freeze instantly depending on the freezer temperature.
Read less
Hoar frost covers lilac bush in the hay field.
Frost is the solid deposition of water vapor from humid air. It is formed when the temperature of a solid surface is below the freezing point of water and also below the frost point. The size of frost crystals varies depending on the time they have been building up and the amount of water vapour available. Frost crystals are translucent, but scatter light in many directions, so that a coating of frost appears white. There are many types of frost, such as radiation and window frost. Frost may damage crops or reduce future crop yields, hence farmers may take measures to prevent it forming.
Hoar frost (also called radiation frost or hoarfrost or pruina) refers to the white ice crystals, loosely deposited on the ground or exposed objects, that form on cold clear nights when heat is lost into the open sky causing objects to become colder than the surrounding air. A related effect is flood frost or frost pocket which occurs when air cooled by ground-level radiation losses travels downhill to form pockets of very cold air in depressions, valleys, and hollows. Hoar frost can form in these areas even when the air temperature a few feet above ground is well above freezing. Nonetheless the frost itself will be at or below the freezing temperature of water.
Hoar frost may have different names depending on where it forms. For example, air hoar is a deposit of hoar frost on objects above the surface, such as tree branches, plant stems, wires; surface hoar is formed by fernlike ice crystals directly deposited on snow, ice or already frozen surfaces; crevasse hoar consists of crystals that form in glacial crevasses where water vapour can accumulate under calm weather conditions; depth hoar refers to cup shaped, faceted crystals formed within dry snow, beneath the surface.
The name hoar comes from an Old English adjective for showing signs of old age, and is used in this context in reference to the frost which makes trees and bushes look like white hair. It may also have association with hawthorn when covered in its characteristic white spring blossom.
Surface hoar is a cause of avalanches when it forms on top of snow. Conditions are ideal for the formation of hoarfrost on cold clear nights, with a very light wind that is able to circulate more humidified air around the snow surface. Wind that is too abrupt will destroy the crystals. When buried by subsequent snows they may remain standing for easy identification, or become laid down, but still dangerous because of the weakness of the crystals. In low temperatures surface hoar can also be broken apart and blown across the surface forming yukimarimo.
Hoar frost also occurs around man-made environments such as freezers or industrial cold storage facilities. It occurs in adjacent rooms that are not well insulated against the cold or around entry locations where humidity and moisture will enter and freeze instantly depending on the freezer temperature.
Read less
Views
322
Likes
Categories
Same photographer See all
Discover more photos See all











































